Often a small business cannot justify the cost of acquiring a static IP from their ISP. It is still possible to host e-mail and other services using a dynamic public IP, but you will need to use a DDNS service (Dynamic Domain Name Service). The following instructions use services offered by No-IP ( www.no-ip.comsee link below), my preference, but similar services are offered by other vendors such as http://www.dyndns.org .
The following assumes you have already purchased a domain name from a registrar. There is no need to host it with your DDNS provider but if they support your domain suffix, such as .com, you can transfer it to them for management simplicity if you wish. You can also purchase a domain through most DDNS service providers if you do not already have one. However, for the purpose of this article it is assumed the domain is with another registrar.

Set up DNS records:
I recommend purchasing and configuring the necessary services first, followed by making the changes with your domain registrar so that there is no interruption of service if the domain name is already in use. You will need to open an account with No-IP and then purchase their Plus Managed DNS service ($24.95/year). To locate, on the No-IP menu choose Services, managed DNS, No-IP Plus, learn more. Then simply enter your public domain name, click “add my domain”, and then proceed to check out.

Once complete, you need to configure your DNS records. To access the management screen select “Your No-IP” from the top of the screen, DNS hosting, then modify next to your domain name. No-IP sets up assumed common DNS records like ftp.DomainName.comwhich you can leave, or I would recommend removing and just creating the records you need. Click on “Add a host” . In the dropdown list to the right of Hostname, select your domain. In the window to the left enter the name you will use to connect to your server. This can be anything you like but if using a certificate, self-signed or purchased, it must match this name. Common names are mail, the name of the server, or the default with Small Business Server 2008 is “remote”. Click the “Create Host” button at the bottom to save.

Next you need to create an MX record for mail delivery. The MX record would usually uses the Host record you just created, but if you plan to use a different Host name you need to repeat the above process for the additional Host record.
Return to the “Managed Hosts” page and click on “Modify” next to DomainName.com (the root). In the bottom section of the page under mail options enter the Host record you created (not an IP) and click the Update button.

Chances are if you are using a DDNS service you have only one server (one MX record). You may want to consider a backup MX service such as the one offered by No-IP. This is added as a second, lower priority, MX record and in the event your server is off line, the No-IP service stores any mail destined for your server for up to 7 days until your server is back on line. It then automatically forwards all mail to your server. One of the nice features of the No-IP Backup MX service over others is it offers an online usage report. Often you may not be aware your server was off-line due to an ISP outage. The Usage report will record when and how long.
If you have other services such as a web page hosted with a 3rd party or at a second site, you need to create another host record for www.DomainName.compointing to the appropriate IP. If not an IP and you need to redirect to another URL you can use the “Web Redirect” option.
Configure the DDNS client:
The DDNS client needs to be downloaded and installed on a PC or server on your network that is always on, and does not sleep or hibernate. It will monitor your public IP and update No-IP should the IP change. Many newer routers support DDNS services internally, but they require the “Custom DNS” option for No-IP, which most do not. The best bet is to install the No-IP client on your server. It can be downloaded from the No-IP site by choosing the Download tab on the home page.
Once installed, start the No-IP DUC client from the programs menu. Enter your e-mail address and password you used to set up your No-IP account. There should be a popup window as below, but if not click “Select Host” in the client management window. Check the box next to the Host record or records you wish to update with this public IP, and save. I do not recommend choosing the root domain unless you want ALL traffic for your domain directed to this IP.
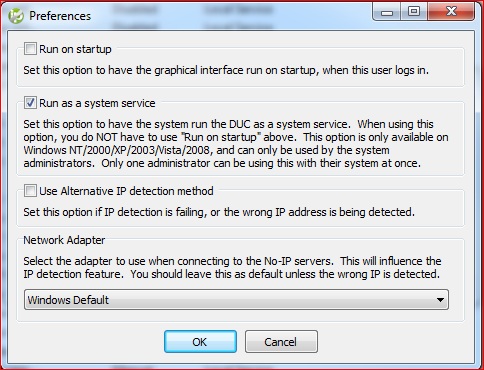
Next you need to make sure this runs at all times even upon reboot by running the No-IP client as a service. In the No-IP client select file, preferences, check the box “Run as a system service”. At the bottom, if there is only one network adapter installed, you can leave as “Windows Default”. If more than one network adapter select the appropriate one from the drop down list, then click OK to save. This should be the Internet facing network adapter.
You can close the No-IP client but for future reference note there are some useful troubleshooting tools built in for testing your server, especially to see if the appropriate ports are open for the services you are offering via the Internet.

Set Domain to use No-IP DNS servers::
The final step is to change your Domain registrar to use No-IP’s DNS servers. With many registrars such as http://www.networksolutions.com you can make these entries yourself, but with some others you have to call or open a trouble ticket and have the service provider make the changes. No-IP’s DNS servers are listed below. You do not have to use all 5.
ns2.no-ip.com (204.16.254.6)
ns1.no-ip.com (69.72.255.6)
ns3.no-ip.com (69.65.5.106)
ns4.no-ip.com (72.5.169.6)
ns5.no-ip.com (75.102.59.82)
Note: DNS changes can take up to 48 hours to propagate the various Internet DNS servers, however usually less than 8 hours. One of the advantages of a DDNS service is in the future if your IP changes due to a move or ISP change, the DNS changes are immediate. For this reason some technicians choose to use a DDNS service even if using a static IP as it can make for faster recovery in a disaster situation, when a server has to be set up in a new location.
One possible issue with hosting your own services and using a dynamic IP is the ISP blocking specific ports such as 25 which will not allow you to host a mail server. There are services such as NO-IP’s “Mail Reflector” which allow you to use ports other than the standard port 25.
SSL Certificates:
Once your DDNS service is configured you may want to purchase a 3rd party SSL certificate from a vendor such as www.godaddy.com . The certificate eliminates the need of installing the SBS self-signed certificate on remote devices connecting to your server. This will work with a dynamic IP and a DDNS service but as mentioned the name created by the SBS to be used remotely (in our example remote.DomainName.com), the public DNS record, and the SSL certificate must all be the same. For details regarding installing an SSL certificate on SBS 2008/2011 see: https://blog.lan-tech.ca/2012/05/17/sbs-2008-2011-adding-an-ssl-certificate/
















